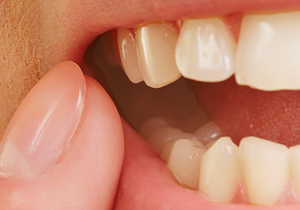
Swollen and painful gums are symptoms of periodontal disease, an inflammatory gum disease. Swelling occurs from an auto-immune response of the body reacting to an infection. Infections are noticeable through pain, redness, and warmth. If the infection is left untreated, it can impact the bone near the teeth. The body’s immune system wants to rid the bone of the harmful material the bacteria is creating. Over time, bone loss will develop.
Inflammation in the gums also is associated with atherosclerosis, the occurrence of fatty deposits inside the body’s arteries. Inflammation coincides with an increase of the blood protein CRP (C-reactive protein), produced by the liver. The more inflammation there is, the more the liver produces CRP. The more CRP present, the more likely cardiovascular disease is present, along with related problems. CRP production is also related to arthritis, auto-immune disorders, and intestinal issues.
Scientists are currently looking into the relationship between periodontal inflammation and CRP levels and the effects outside of the oral cavity. Links have already been discovered between periodontal disease and pancreatic cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
If inflammation is left untreated, gums can develop pockets that provide the perfect breeding ground for infection. The longer the infection persists, the more likely bone loss will arise, eventually causing tooth loss.
It is indispensable to practice preventive dental care daily at home and have regular visits to the dentist. Dental appointments should include an exam, cleaning, and full mouth x-rays, along with vital knowledge and instruction on how to properly care for teeth and gums at home. It is also very important to see your dentist ASAP if a tooth suddenly becomes sensitive or you see any other changes.